In July 2013, Alex Webb asked whether Grasshopper was initially developed as a teaching tool to show how information flowed through commands.
David Rutten denied this.
[Grasshopper] was developed for Rhino customers as a way to automate tasks without the need to write textual code. We expected that some of our users who were interested in RhinoScript or C# or VB.NET would be interested, but we certainly didn't think that it would be taught (at gunpoint apparently in some universities) to the masses.
Originally, the product was called Explicit History1, because it was a different approach to Rhino's native (implicit) history feature. Rhino history is recorded while you model and can then be played back, Grasshopper history is defined from scratch while the model is created as an afterthought.
I found this while putting together the episode notes for a conversation with Andy Payne on the Getting Simple podcast, where he shares curiosities of Grasshopper's origins and its transition from Explicit History to the initial Grasshopper release, Grasshopper 1, and Grasshopper 2.
In the publication, David Rutten adds that Explicit History was initially called Semantic Modeling, "but that never even made it out of the building." ↩
Just by adding simple codes at the end of the shortcut path, you can make Rhino run commands at startup, or customize things [removing the splash screen for example].
To run Grasshopper when Rhino starts and remove the Splash Screen, you can just add the following to the back of the path in your Rhino shorcut — right click the shortcut and edit the path.
/runscript="!_grasshopper" /nosplash
This article is part of a series of posts about efficient architectural methods, workflows and tools, titled Getting Architecture Done.
If you want to be notified when any other articles of the same series are posted, go ahead an subscribe here.

In the next months—of February and March—PercepciónDigital will be teaching NURBS modeling with Rhino and algorithmic design with Grasshopper in Málaga, at the Metropolitan Design Lab.
The course is thought for designers who want to learn how to implement advanced 3D-modeling techniques and algorithmic design in their design projects—skills that I believe contribute adding freedom to any computer-driven design process.
Also, it is a good opportunity to get introduced to the world of parametric design.
Check out the Full Course Information

Last February, I shared my Compression design on Dribbble. The following screenshots illustrate the steps to generate the geometry. The curves were made using Rhino 5 and Grasshopper.
The whole design is parametric, as the geometry is based in modifiable parameters which can be altered after the design is finished to adjust the final result.
The parameters here are four lines, which can be moved in Rhino, rotated or scaled, and are referenced into the Grasshopper definition.

Then, the lines are subdivided in equidistant segments, with a parameter of the number of points. In this case, there are 76 segments on each line.
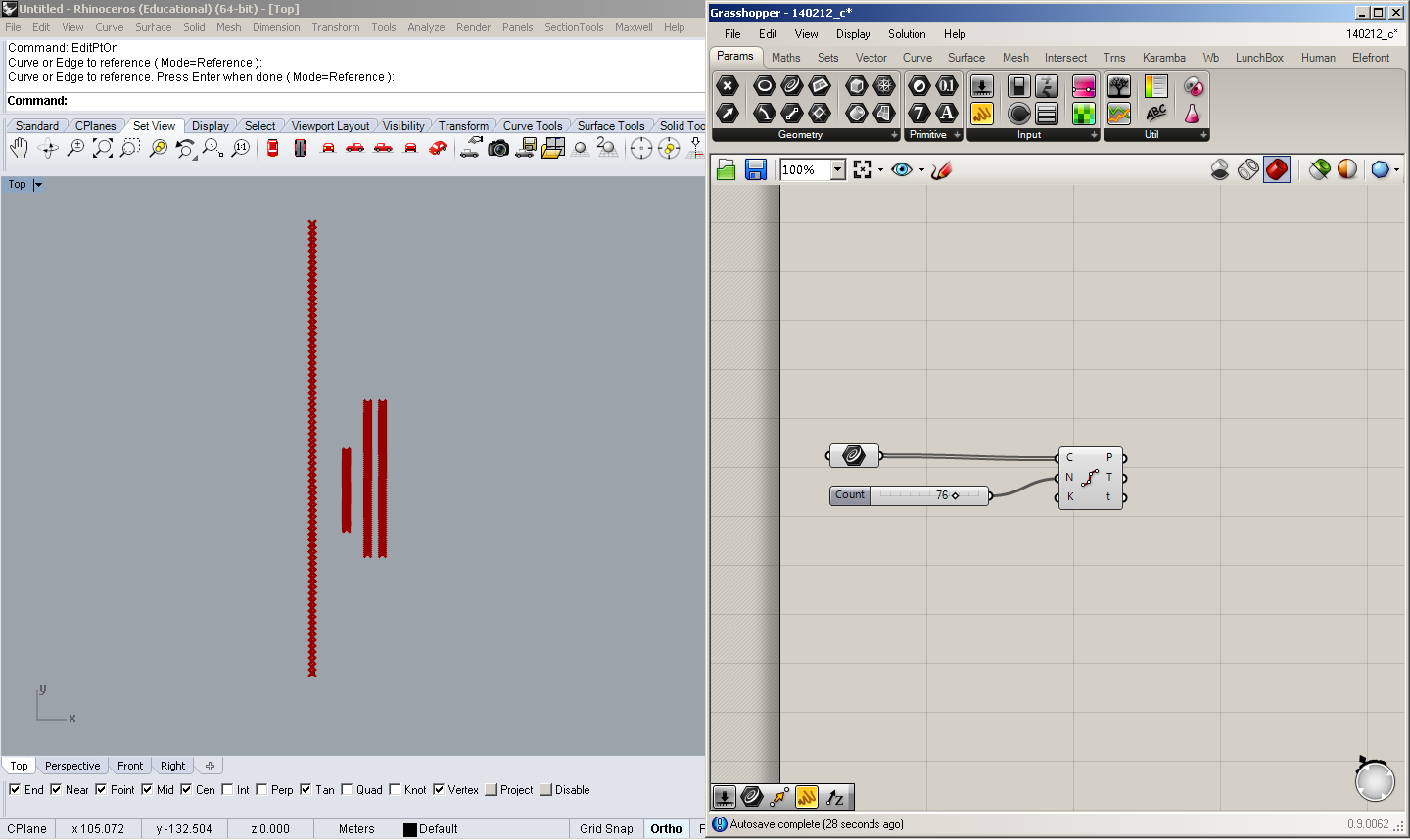
Using the Interpolate Curve component, the subdividing points are joined with spline curves.

Now, a surface created in Rhino is referenced in Grasshopper, which will act as our canvas, trimming the outer segments of the curves.

With the component Project, the curves are projected on the surface, and the outer segments disappear.


Now that the parametric definition is finished, we can adjust the initial parameters. This is, the initial lines and the amount of segments on each of them.

If you liked this post, please share it or let me know what you think. Thanks for reading!

Grasshopper is an algorithmic modeling plugin for Rhino that uses a visual programming language, developed by David Rutten as an official plugin of Rhino. It is a parametric design tool.
Grasshopper allows you to reference Rhino geometry objects from it (points, curves, surfaces, etc.), create geometry or bake Grasshopper geometry back into Rhino.
Here are some reasons why I think Grasshopper could benefit your architecture design process, making things easier, faster and non-repetitive.
Imagine having to draw 1000 perpendicular lines to a given line at a certain distance. Lets call that distance X. Surely, you are not going to do this with a pencil and a ruler.
Assuming you do not use any parametric tool such as Grasshopper, you would get a CAD tool and draw one perpendicular line, then copy it 999 times one at a time. In the best case, you can use the matrix function to repeat the action 999 times.
In Grasshopper, the workflow is different. You would say: Divide this line into X segments, then Draw a perpendicular line in each of the subdividing points. After creating this parametric model, where the variable X is the number of segments subdividing your line, you can save the model for later use, which will allow you to modify the number of segments –initially 1000– to any other number of your choice, 5000 for instance. This is a really simple example, and is already pretty useful.
Following the argument of the previous point, parametric design is said to be for lazy people, who do not like to ever repeat the same thing they have done before –as happens with programming.
With Grasshopper, you can create your own modules to perform a certain task. A module designed for the previous example could be called something like Draw X Perpendiculars Lines Of a Line.
Each module works as a function that gets inputs as variables and returns solutions or results which are called outputs. In the previous example, the inputs are the number of perpendiculars (X) and the line you are going to draw them into. The outputs resulting from the module are the perpendicular lines.
As happens in the open-source code movement –where programmers share the source code of their projects– many designers share awesome tools and plugins and release them for public use (these does not mean that they always give away the code of their tools).
To be more specific, plugins are available to download, that will add new modules created by other people to your Grasshopper. This means that somebody, or yourself, could have already created the module we mentioned before, X perpendicular lines in line. So you could just go, download it, and use it in your project.
So, you may get done certain design in CAD in lets say 1 hour. Depending on the complexity of the design, you could get done a parametric model of the same design in the same time, maybe in more, or maybe in less.
Why is the parametric model a benefit then? Because after you have the model, it will probably take you less than a minute to change your variables in order to generate different possibilities, while in CAD you would have to spend a whole hour again for each new iteration you want to test.
Once it is done, a parametric model allows for extremely fast iterations, whereas in CAD, everything has to be redrawn over and over manually. Drawing manually repetitive things is one of the tasks algorithmic design tries to avoid.
This article is part of a series of posts about architectural methods, workflows and tools, titled Getting Architecture Done.
If you want to be notified when any other articles of the same series are posted, go ahead an subscribe here.